使用emplace_back 和push_back的性能差别来自于,向vector中添加自定义类型的新对象时:
- 前者支持直接传入参数,可以在
vector内直接构造对象; - 后者不支持直接传入参数,所以只能先构造临时对象,调用类的拷贝构造函数将临时对象拷贝到
vector中,之后析构临时对象。
下面是笔者的测试代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define RESET "\x1B[0m"
#define RED "\x1B[31m"
#define GRN "\x1B[32m"
#define YEL "\x1B[33m"
#define BLU "\x1B[34m"
#define MAG "\x1B[35m"
#define CYN "\x1B[36m"
#define WHT "\x1B[37m"
bool is_reserve = false;
class Point {
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
// 构造函数
Point(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {
printf("%sConstruct (%d, %d)%s\n", GRN, x, y, RESET);
}
// 拷贝构造函数
Point(const Point &p) : x(p.x), y(p.y) {
printf("%sCopy (%d, %d)%s\n", BLU, x, y, RESET);
}
// 移动构造函数
/*
Point(Point &&rhs) : x(rhs.x), y(rhs.y) {
printf("%sMove (%d, %d)%s\n", YEL, x, y, RESET);
}
*/
// 析构函数
~Point() { printf("%sDestruct (%d, %d)%s\n", RED, x, y, RESET); }
};
struct EPNotWork {
int noConstructor;
};
void push_back_test() {
vector<Point> vec;
if (is_reserve) {
vec.reserve(3);
}
vec.push_back(Point(1, 2));
cout << endl;
vec.push_back(Point(2, 3));
cout << endl;
vec.push_back(Point(3, 4));
cout << endl;
}
void emplace_back_test() {
vector<Point> vec;
if (is_reserve) {
vec.reserve(3);
}
vec.emplace_back(1, 2);
cout << endl;
vec.emplace_back(2, 3);
cout << endl;
vec.emplace_back(3, 4);
cout << endl;
}
void test_efficency() {
cout << "push_back_test:" << endl;
push_back_test();
cout << endl;
cout << "emplace_back_test:" << endl;
emplace_back_test();
}
void test_for_strcut() {
vector<EPNotWork> vec;
vec.push_back({0});
// Error
// vec.emplace_back({0});
// No Error after declare Struct name explicitly
vec.emplace_back<EPNotWork>({0});
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
cout << "No reserve" << endl;
test_efficency();
cout << endl;
cout << "Reserve" << endl;
is_reserve = true;
test_efficency();
return 0;
}
输出:
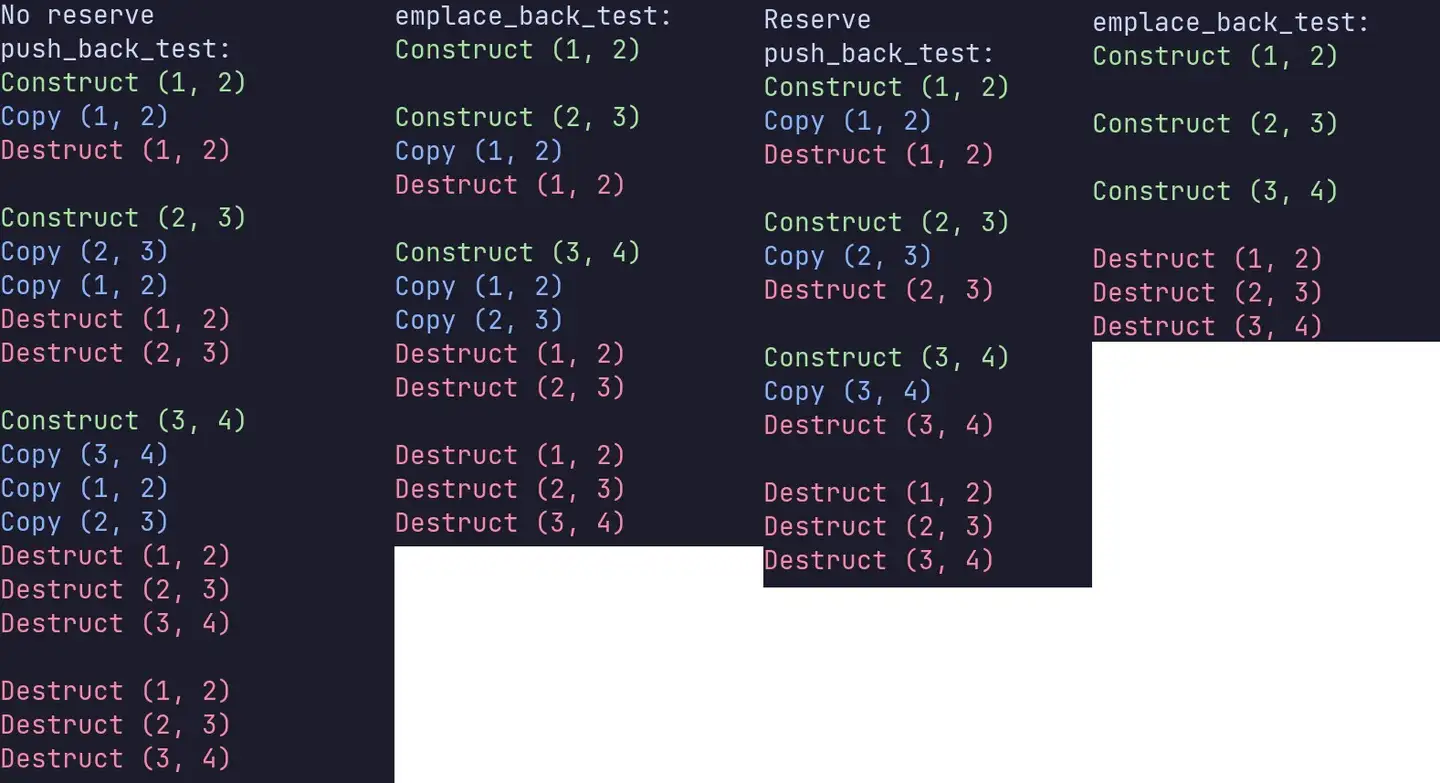
因为传给push_back的是匿名对象(右值rvalue,更确切来讲是将亡值xvalue),所以相应调用的是接收右值作为参数的push_back的重载。如果取消Point类中移动构造函数的注释,push_back则会调用移动构造函数。
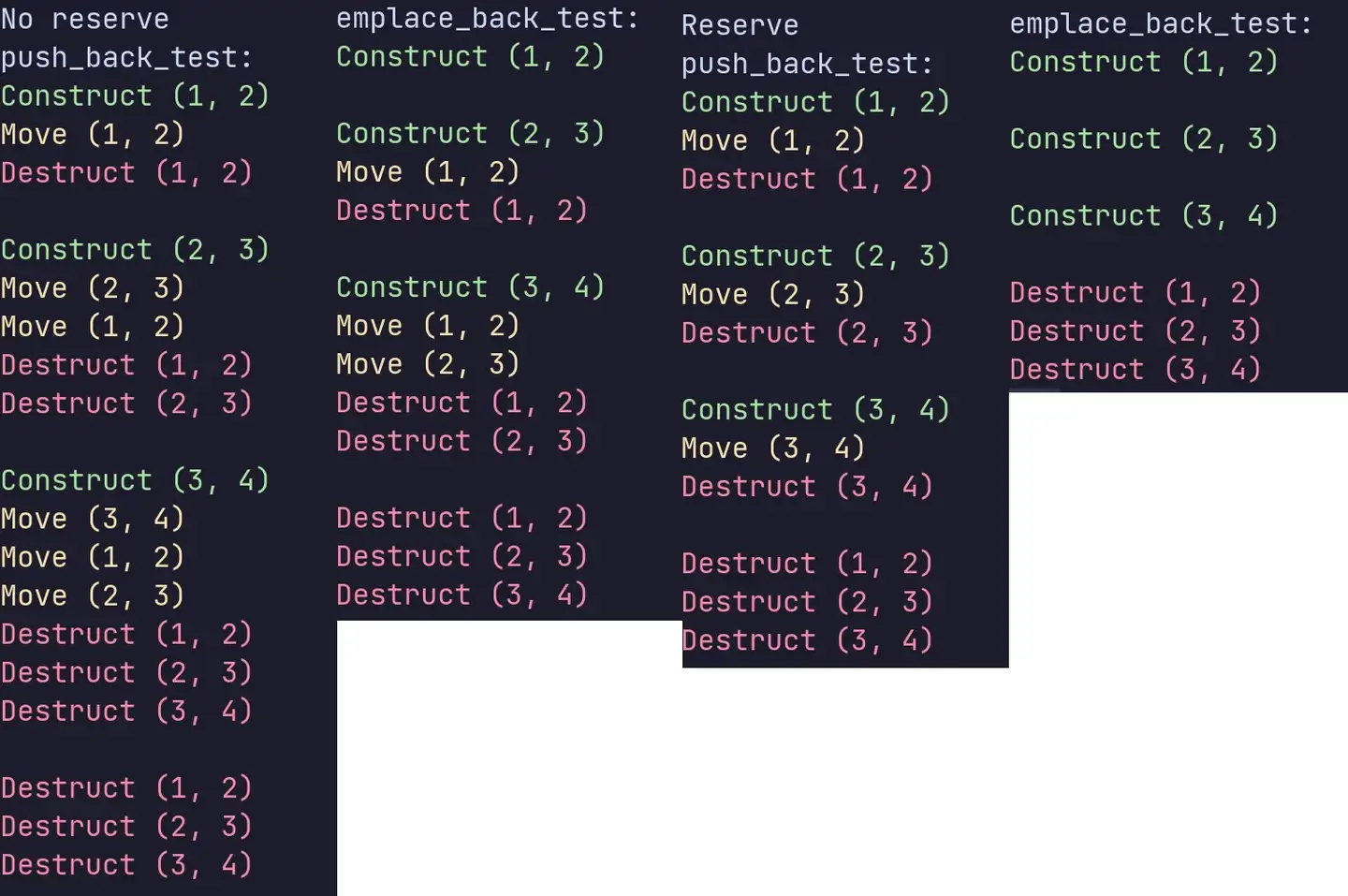
由此可见,只要是需要创建新的自定义类型的对象并将其加入vector中时,push_back都无法摆脱其需要调用2次构造函数(1次普通构造函数、1次拷贝或移动构造函数)和1次析构函数的行为。
之所以要强调是加入新对象的原因在于如果加入已经构造过的对象,二者不会有任何的性能差距。
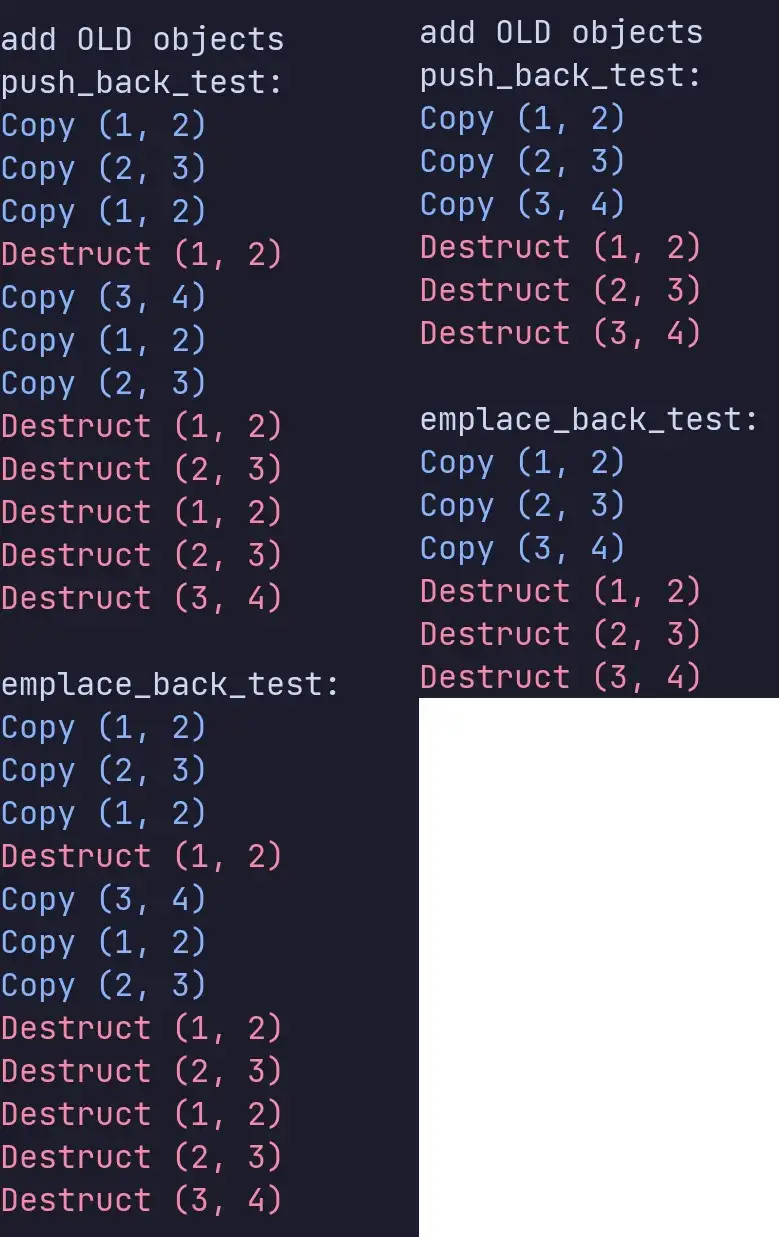
在性能上还有一点需要注意的是:vector 在创建之后不使用reserve 预留大小的话,每次添加新元素都会拷贝旧vector 中的所有元素到新的vector 中。