Overview
MLflow是一个用于管理机器学习全生命周期的框架。
其主要的作用是:
- 完成训练和测试过程中不同超参数的结果的记录、对比和可视化——
MLflow Tracking - 以一种可复现重用的方式包装 ML 代码——
MLflow Projects - 简化模型部署的难度——
MLflow Models - 提供中心化的模型存储来管理全生命周期——
MLflow Model Registry
现在主要用到的是第三个,所以先记录Models的用法
MLflow Models
MLflow Models本质上是一种格式,用来将机器学习模型包装好之后为下游的工具所用。
这种格式定义了一种惯例来让我们以不同的flavor保存模型进而可以被下游工具所理解。
存储格式
每个MLflow Model是一个包含任意文件的目录,根目录之下有一个MLmodel文件,用于定义多个flavor。
flavor是MLflow Model的关键概念,抽象上是部署工具可以用来理解模型的一种约定。
MLflow定义了其所有内置部署工具都支持的几种标准flavor,比如描述如何将模型作为Python函数运行的python_function flavor。
目录结构示例如下:
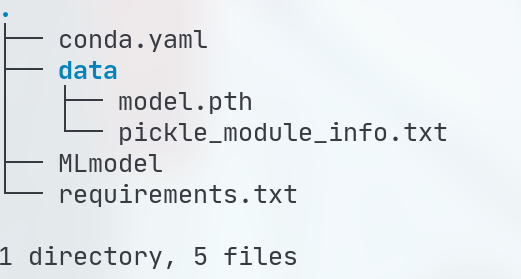
MLmode文件内容示例如下:
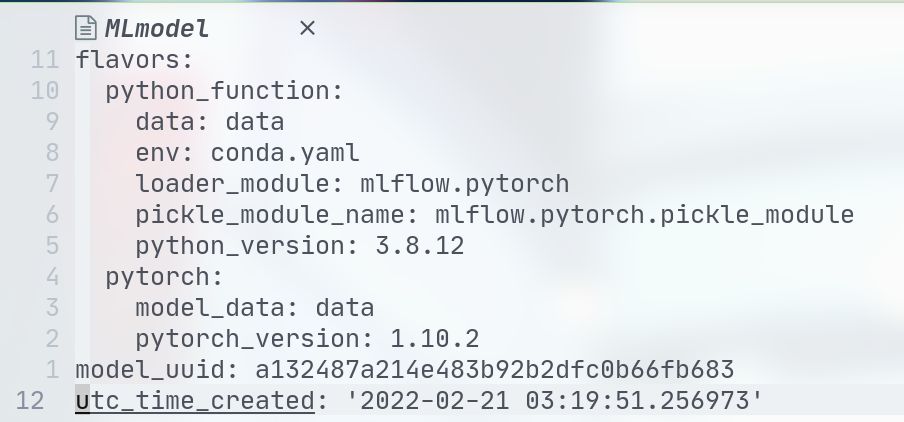
这个模型可以用于任何支持pytorch或python_function flavor的工具,例如可以使用如下的命令用python_function来 serve 一个有python_function flavor的模型:
mlflow models serve -m my_model
Model Signature
模型的输入输出要么是column-based,要么是tensor-based。
column-basedinputs and outputs can be described as a sequence of (optionally) named columns with type specified as one of theMLflow data type.tensor-basedinputs and outputs can be described as a sequence of (optionally) named tensors with type specified as one of thenumpy data type.
Signature Enforcement
Schema enforcement checks the provided input against the model’s signature and raises an exception if the input is not compatible. It only works when using MLflow model deployment tools or loading models as python_function. It has no impact on native model.
Name Ordering Enforcement
The input names are checked against the model signature. If there are any missing inputs, MLflow will raise an exception. Extra inputs will be ignored. Prioritized method is matching by name if provided in input schema, then according to position.
Input Type Enforcement
For column-based signatures, MLflow will perform safe type conversions if necessary. Only lossless conversions are allowed.
For tensor-based signatures, type checking is strict(any dismatch will throw an exception).
Handling Integers With Missing Values
Integer data with missing values is typically represented as floats in Python.
Best way is to declare integer columns as doubles whenever there can be missing values.
Handling Data and Timestamp
Python has precision built into the type for datatime values.
Datetime precision is ignored for column-based model signature but is enforced for tensor-based signatures.
Log Models with Signatures
Pass signature object as an argument to the appropriate log_model call to include a signature with model. The model signature object can be created by hand or inferred from datasets with valid model inputs and valid model outputs.
Column-based example
The following example demonstrates how to store a model signature for a simple classifier trained on the Iris dataset:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
import mlflow
import mlflow.sklearn
from mlflow.models.signature import infer_signature
iris = datasets.load_iris()
iris_train = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
clf = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=7, random_state=0)
clf.fit(iris_train, iris.target)
signature = infer_signature(iris_train, clf.predict(iris_train))
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(clf, "iris_rf", signature=signature)
The same signature can be created explicitly as follows:
from mlflow.models.signature import ModelSignature
from mlflow.types.schema import Schema, ColSpec
input_schema = Schema([
ColSpec("double", "sepal length (cm)"),
ColSpec("double", "sepal width (cm)"),
ColSpec("double", "petal length (cm)"),
ColSpec("double", "petal width (cm)"),
])
output_schema = Schema([ColSpec("long")])
signature = ModelSignature(inputs=input_schema, outputs=output_schema)
Tensor-based example
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.utils import to_categorical
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Dense, Flatten
from keras.optimizers import SGD
import mlflow
import mlflow.keras
from mlflow.models.signature import infer_signature
(train_X, train_Y), (test_X, test_Y) = mnist.load_data()
trainX = train_X.reshape((train_X.shape[0], 28, 28, 1))
testX = test_X.reshape((test_X.shape[0], 28, 28, 1))
trainY = to_categorical(train_Y)
testY = to_categorical(test_Y)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_uniform', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
model.add(MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(100, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_uniform'))
model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
opt = SGD(lr=0.01, momentum=0.9)
model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(trainX, trainY, epochs=10, batch_size=32, validation_data=(testX, testY))
signature = infer_signature(testX, model.predict(testX))
mlflow.keras.log_model(model, "mnist_cnn", signature=signature)
The same signature can be created explicitly as follows:
import numpy as np
from mlflow.models.signature import ModelSignature
from mlflow.types.schema import Schema, TensorSpec
input_schema = Schema([
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.uint8), (-1, 28, 28, 1)),
])
output_schema = Schema([TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.float32), (-1, 10))])
signature = ModelSignature(inputs=input_schema, outputs=output_schema)
Model Input Example
Model inputs can be column-based (i.e DataFrame) or tensor-based (i.e numpy.ndarrays).
A model input example provides an instance of a valid model input which can be stored as separate artifact and is referenced in the MLmodel file.
Log Model with column-based example
An example can be a single record or a batch of records. The sample input can be passed in as a Pandas DataFrame, list or dict. The given example will be converted to a Pandas DataFrame and then serialized to json using the Pandas split-oriented format.
input_example = {
"sepal length (cm)": 5.1,
"sepal width (cm)": 3.5,
"petal length (cm)": 1.4,
"petal width (cm)": 0.2
}
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(..., input_example=input_example)
Log Model with Tensor-based example
An example must be a batch of inputs. The axis 0 is the batch axis by default unless specified otherwise in the model signature. The sample input can be passed in as a numpy ndarray or a dict mapping a string to a numpy array.
# each input has shape (4, 4)
input_example = np.array([
[[ 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 134, 25, 56],
[253, 242, 195, 6],
[ 0, 93, 82, 82]],
[[ 0, 23, 46, 0],
[ 33, 13, 36, 166],
[ 76, 75, 0, 255],
[ 33, 44, 11, 82]]
], dtype=np.uint8)
mlflow.keras.log_model(..., input_example=input_example)
Model API
MLflow includes integrations with several common libraries. For example, mlflow.sklearn contains save_model, log_model, and load_model functions for scikit-learn models.
Additionally, we can use mlflow.models.Model class to create and write models which has 4 key functions:
add_flavorto add a flavor to the model. Eachflavorhas astringname and adictof key-value attributes, where the values can be any object that can be serialized to YAML.saveto save the model to a local directory.logto log the model as an artifact in the current run usingMLflow tracking.loadto load a model from a local directory or from an artifact in a previous run.
Pytorch
mlflow.pytorch module defines utilities for saving and loading MLflow Models with the pytorch flavor.
We can use mlflow.pytorch.save_model() and mlflow.pytorch.log_model() methods to save pytorch models in MLflow format.
We can use mlflow.pytorch.load_mode() to load MLflow Models with pytorch flavor as pytorch model objects. This loaded PyFunc model can be scored with both DataFrame input and numpy array input.