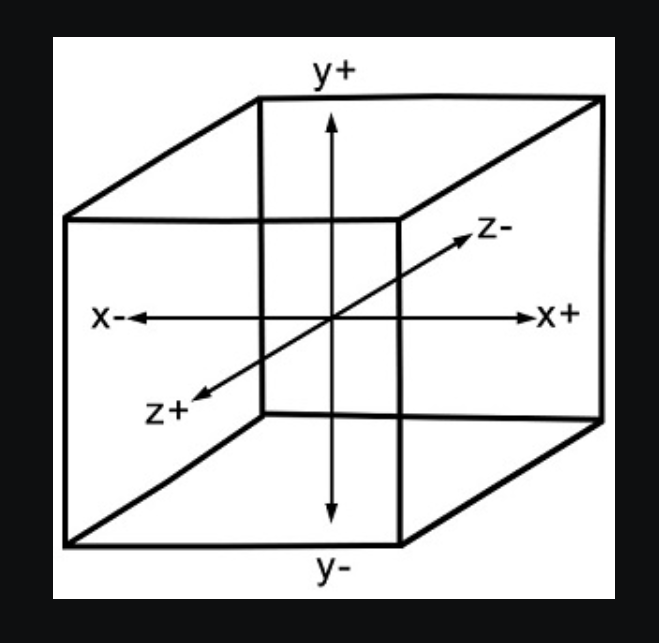
Coordinate System
There are x, y, z axes in WebGL, where the z axis signifies depth. The coordinates in WebGL are restricted to (1, 1, 1) and (-1, -1, -1). Positive value meaning: z: near viewer. x: near right. y: near top.
Graphics System
Vertices
To draw a polygon, we need to mark the points on the plane and join them to form a desired polygon.
A vertex is a point which defines the conjunction of the edges of a 3D object.
Use javascript arrays to stores points’ coordinates like [0.5, 0.5, 0.5].
Indices
The numerical values which are used to identify the vertices is call Indices.
Arrays
There are no predefined methods in WebGL to render the vertices directly.
let vertices = [0.5, 0.5, 0.1, -0.5, 0.5, -0.5];
Buffers
Buffers are the memory areas of WebGL that hold the data. There are various buffers:
drawing bufferframe buffervertex bufferindex buffer
The vertex buffer and index buffer are used to describe and process the geometry of the model, stores data about vertices and indices respectively.
The frame buffer is a portion of graphics memory that hold the scene data. This buffer contains details such as width and height of the surface (in pixels), color of each pixel, depth and stencil buffers.
Mesh
The WebGL API provides two methods to draw 2D or 3D objects:
drawArrays()drawElements()
They accept a parameter called mode using which you can select the object you want to draw.
mode: points or lines or triangles
We can construct primitive polygons using points, lines and triangles.
Thereafter, we can form a mesh using these polygons.
A 3D object drawn using primitive polygons is called a mesh.
Shader Programs
Since WebGL uses GPU accelerated computing, the information about these triangles should be transferred from CPU to GPU which takes a lot of communication overhead.
WebGL provides a solution to reduce the communication overhead. Since it uses ES SL(Embedded System Shader Language) that runs on GPU, we write all the required programs to draw graphical elements on the client system using shader programs(OpenGL ES Shader Language).
Shader is a snippet that implements algorithms to get pixels for a mesh.
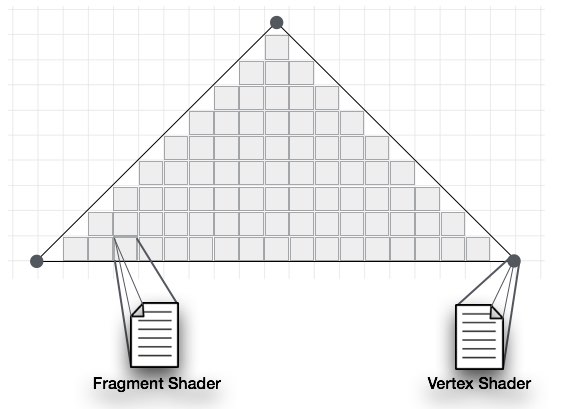
There are two types of shaders: Vertex Shader and Fragment Shader.
Vertex Shader
- called on every vertex.
- used to transform the geometry from one place to another.
- handle the data of each vertex such as vertex coordinates, normals, colors, and texture coordinates.
- vertex transformation
- normal transformation and normalization
- texture coordinate generation
- texture coordinate transformation
- lighting
- color material application
Fragment Shader(Pixel Shader)
A mesh is formed by multiple triangles. The surface of each of the triangles is known as a fragment.
Fragment shader is the code that runs on all pixels of every fragment.
It is written to calculate and fill the color on individual pixels.
- operations on interpolated values
- texture access
- texture application
- fog
- color sum
OpenGL ES SL Variables
To handle the data in the shader programs, ES SL provides three types of variables.
Attributes: hold the input values of the vertex shader program. Attributes point to the vertex buffer objects that contains per-vertex data.
Uniforms: hold the input data that is common for both vertex and fragment shaders, such as light position, texture coordinates and color.
Varyings: used to pass the data from the vertex shader to the fragment shader.