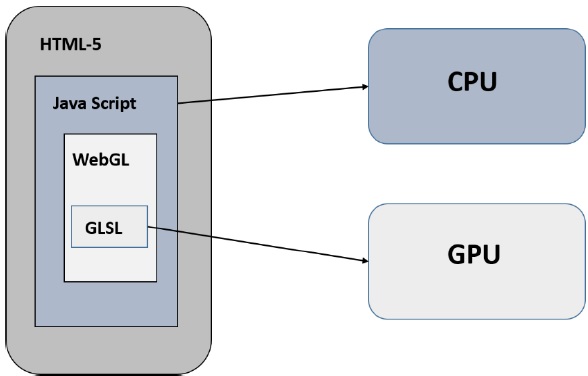
Structure of WebGL Application
WebGL application code is a combination of JavaScript and OpenGL Shader Language.
- JavaScript is required to communicate with the CPU.
- OpenGL Shader Language is required to communicate with the GPU.
Samples
2D coordinates
<!doctype html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas width="300" height="300" id="my_canvas"></canvas>
<script>
// 1. Prepare the canvas and get context
let canvas = document.getElementById("my_canvas");
let gl = canvas.getContext("experimental-webgl");
// 2. Define the geometry and store it in buffer objects
let vertices = [
-0.5,
0.5, // vertex 1
-0.5,
-0.5, //
0.0,
-0.5,
];
// Create buffer object
let vertex_buffer = gl.createBuffer();
// Bind an empty array buffer to it
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertex_buffer);
// Pass the vertices data to the buffer
gl.bufferData(
gl.ARRAY_BUFFER,
new Float32Array(vertices),
gl.STATIC_DRAW,
);
// Unbind the buffer
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, null);
// 3. Create and compile Shader programs
// Vertex shader source code
let vertCode =
"attribute vec2 coordinates;" +
"void main(void) {" +
" gl_Position = vec4(coordinates, 0.0, 1.0);" +
"}";
// Create a vertex shader object
let vertShader = gl.createShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER);
// Attach vertex shader source code
gl.shaderSource(vertShader, vertCode);
// Compile the vertex shader
gl.compileShader(vertShader);
// Fragment shader source code
let fragCode =
"void main(void) {" + "gl_FragColor = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1);" + "}";
let fragShader = gl.createShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER);
gl.shaderSource(fragShader, fragCode);
gl.compileShader(fragShader);
// Create a shader program object to store combined shader program
let shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
// Attact vertex and fragment shader
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragShader);
// Link both programs
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Use the combined shader program object
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// 4. Associate the shader programs to buffer objects
// Bind vertex buffer object
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertex_buffer);
// Get the attribute location
let coord = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, "coordinates");
// Point an attribute to the currently bound VBO
gl.vertexAttribPointer(coord, 2, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0);
// Enable the attribute
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(coord);
// 5. Drawing the required object (triangle)
// Clear the canvas
gl.clearColor(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.9);
// Enable the depth test
gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST);
// Clear the color buffer bit
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Set the view port
gl.viewport(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
// Draw the triangle
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
</script>
</body>
</html>